Subsections of RBAC
Service Accounts
The basic unit in Kubernetes is a Pod. Pods runs inside a namespace. Every namespace have a default service account.
Why we need service account?
If your workload needs to access the Kubernetes API, then we need a mechanism to authenticate and authorize the request. Here we can use the service account and assign permissions to it.
This service account can then be used inside a Pod.
Every namespace have a default service account.
ubuntu@cks-master:~$ kubectl get sa
NAME SECRETS AGE
default 0 4d19h
ubuntu@cks-master:~$ Service account
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: mysvcacc
namespace: default
EOFCreate a Pod and use this service account to contact the API
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
run: api-test
name: api-test
spec:
serviceAccountName: mysvcacc
containers:
- image: nginx
name: api-test
EOFThe authentication using service account happens via a signed JWT token which gets mounted inside the Pod.
View token
kubectl exec -it api-test -- cat /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token && echoYou can visit the https://jwt.io/ to and paste the token to see the details.
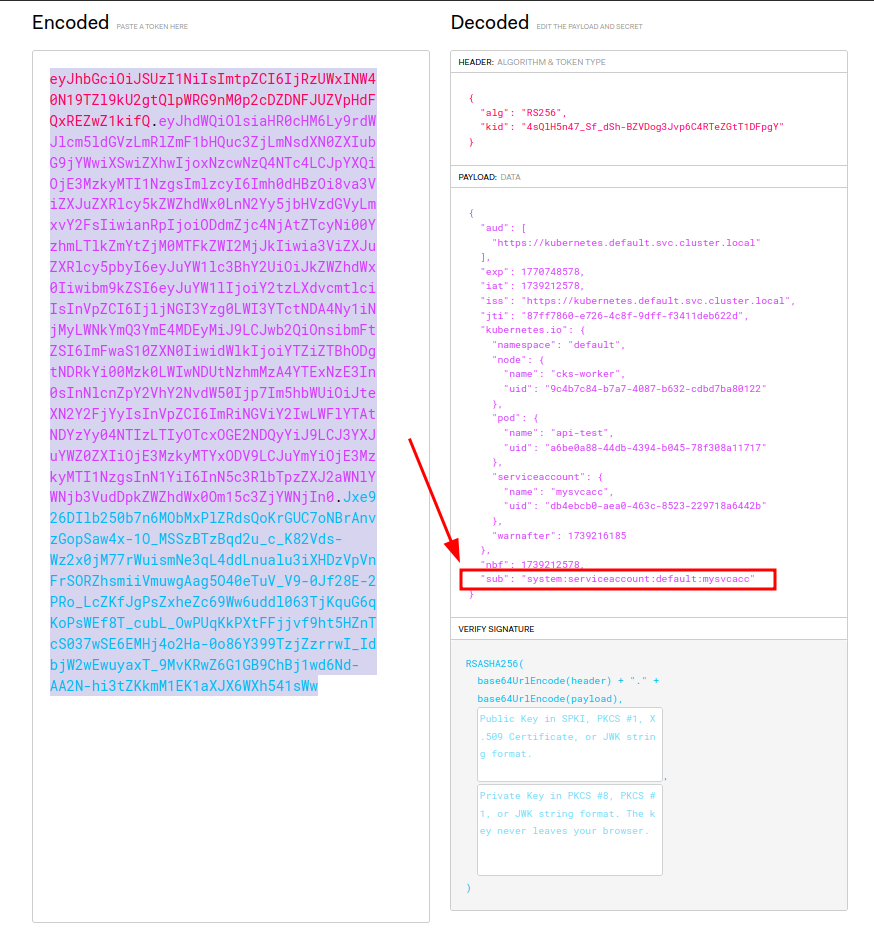
As the screenshot shows, the API service can indentify the token and handle authorization using the “sub” field.
You can control the token mount behavior using below flag.
FIELD: automountServiceAccountToken <boolean>
DESCRIPTION:
AutomountServiceAccountToken indicates whether pods running as this service
account should have an API token automatically mounted. Can be overridden at
the pod level.In which scenario you need to set automountServiceAccountToken to false.
The scenario which your workload don’t have to contact API, but need a service account.
Yes, you can use service account for another scenario where you need an imagePullSecret to pull container images.
Using imagePullSecter in ServiceAccount
kubectl create secret docker-registry myregistrykey --docker-server=<registry name> \
--docker-username=DUMMY_USERNAME --docker-password=DUMMY_DOCKER_PASSWORD \
--docker-email=DUMMY_DOCKER_EMAILkubectl patch serviceaccount mysvcacc -p '{"imagePullSecrets": [{"name": "myregistrykey"}]}'apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2021-07-07T22:02:39Z
name: mysvcacc
namespace: default
uid: 052fb0f4-3d50-11e5-b066-42010af0d7b6
imagePullSecrets:
- name: myregistrykeyAccessing API from Pod
curl -k https://${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST}/api -H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token)"{
"kind": "APIVersions",
"versions": [
"v1"
],
"serverAddressByClientCIDRs": [
{
"clientCIDR": "0.0.0.0/0",
"serverAddress": "192.168.0.175:6443"
}
]
}Role and ClusterRole
The Role is for a namespace and ClusterRole is for entire cluster.
A role maps the permissions to an object.
Below role indicates get and list permissions to object Pod inside the namespace default.
kubectl create role myaccrole --verb=get --verb=list --resource=pod --dry-run=client -o yamlapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: myaccrole
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- get
- listBelow ClusterRole is same as Role, but the difference here is that the ClusterRole can be assigned to many namespaces.
kubectl create clusterrole myaccrole --verb=get --verb=list --resource=pod --dry-run=client -o yamlapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: myaccrole
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- get
- listRoleBinding and ClusterRoleBinding
To bind a role to “User”, “Group”, or “ServiceAccount”
I below example, we will give pod read/list access to service account mysvcacc
kubectl create rolebinding mysvcacc --role=myaccrole --serviceaccount=default:mysvcacc --dry-run=client -o yamlapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: mysvcacc
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: myaccrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: mysvcacc
namespace: default